Did you know that
„Pressure ulcers can occur quickly - between the first hour and 4 to 6 hours after sustained loading.“
„One to four of every ten hospitalized patients develop pressure ulcers.“
„In areas affected by COVID-19 lockdown only 22,6% of patients with chronic wounds went to the wound clinics as usual, and 1 in 10 did not change the wound dressing at all during that whole period.“
It's time to act
Most of the time, pressure sores significantly impact the patients’ morbidity, mortality and quality of life. Once a pressure ulcer has developed, it is important to draw up a coordinated treatment plan to promote healing. The basic prerequisites for wound healing must be met and everything that interrupts this process needs to be avoided. These include pressure ease, a clean wound, functioning circulation, and adequate nutrition in terms of both calories and nutrients along with adequate fluid intake.
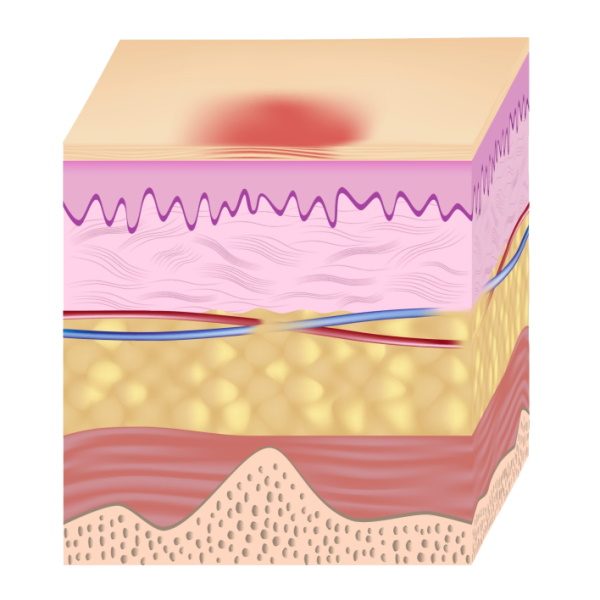
Care of stage 1 pressure sores
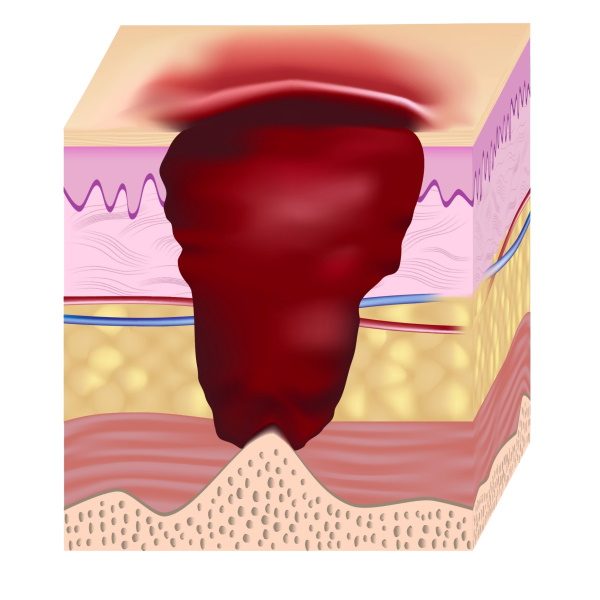
Depending on the extent of tissue damage, pressure sores are categorized into four stages(4). Every stage requires a specific treatment.
How to care for stage 1 pressure ulcers
Prevent and protect: Daily skin hygiene and care
Protect from friction
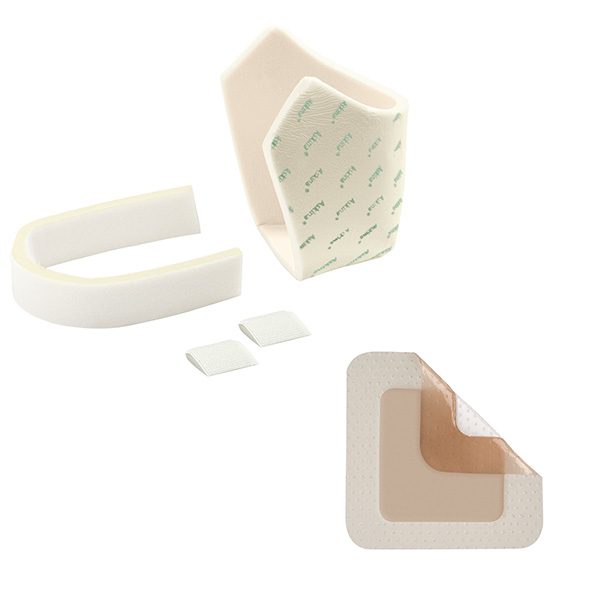
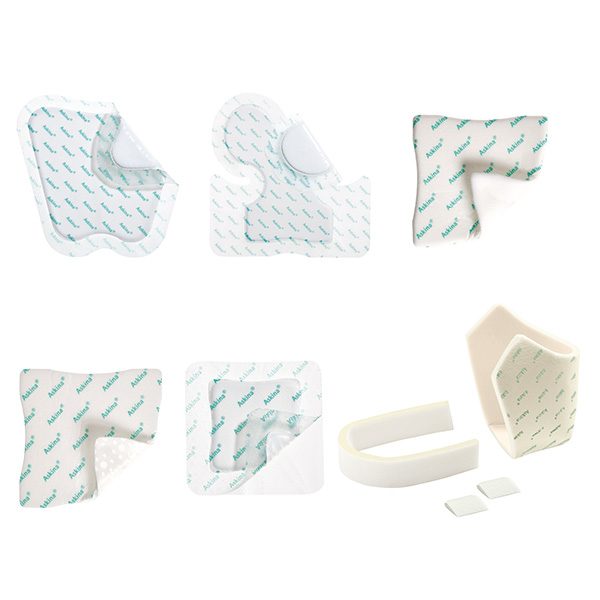
Askina® Heel(10) is a non adhesive hydrocellular heel dressing that protects the heel area from shear stresses and reduces pressure from external forces.
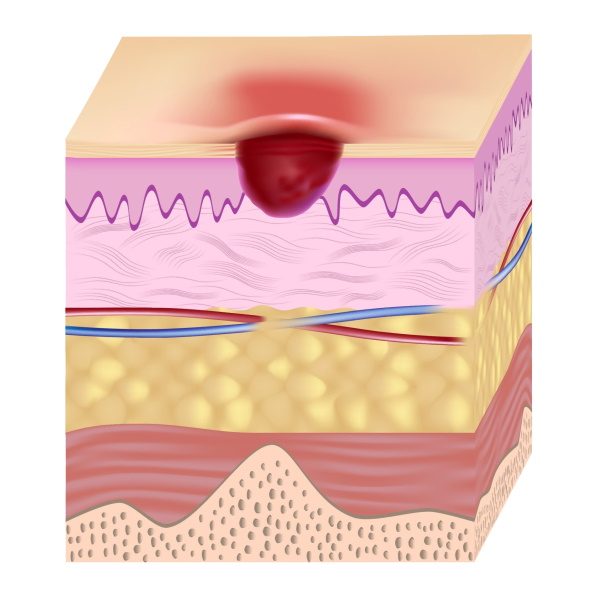
Treatment of stage 2 pressure sores
How to treat stage 2 pressure ulcers
Manage biofilm
Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution(10) is indicated for cleansing irrigation and moistening of acute and chronic wounds.
- Prevents infection(11)
- Helps to prevent biofilm formation
- Reduces healing time(12)
It moistens wound dressings and dissolves encrusted bandages or wound dressings during dressing changes.
Prontosan® Gel X(10) proper wound cleansing is essential. The use of Prontosan® Wound Gel X provides long-lasting cleansing and decontamination of the wound bed between dressing changes.
Prontosan® Debridement Pad(10) has been designed to support the wound bed preparation when used in conjunction with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
Treat local infection
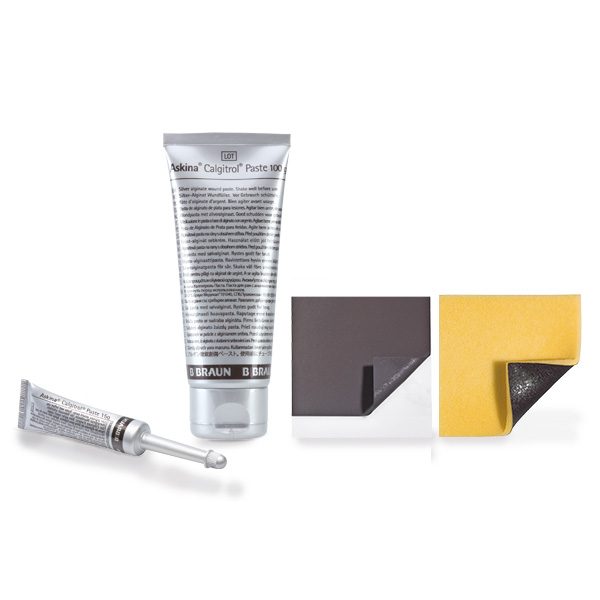
Askina® Calgitrol® is a range of dressings with an ionic silver alginate matrix which in the presence of wound exudate helps maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Paste(13) is a dressing with an ionic silver alginate matrix in a paste form.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Thin(13) is a conformable ionic silver alginate matrix used as a wound bed interface.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Ag(13) integrates an ionic silver alginate matrix on an absorbent polyurethane foam dressing.
Manage wound odour
Askina® Carbosorb(13) is a conformable, sterile wound dressing combining two layers: an absorbent layer and an activated charcoal layer for the absorption of bacterial malodour.
Manage wound exudate
Askina® DresSil Sacrum(13), Askina DresSil(13), Askina® DresSil Border(13) help to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a perfored silicone wound contact layer, a highly absorbent polyurethane foam and a vapor permeable waterproof outer film. Indicated for pressure ulcers (PU), diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), venous leg ulcers (VLU) and 1st/2nd degree burns.
Askina® Foam(13) and Askina® Heel(9) help to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a polyurethane foam wound contact surface with high absorption capacity and a vapour permeable, water and bacteria resistant polyurethane film outer layer. Indicated for pressure ulcers (PU), diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), venous leg ulcers (VLU) and 1st/2nd degree burns.
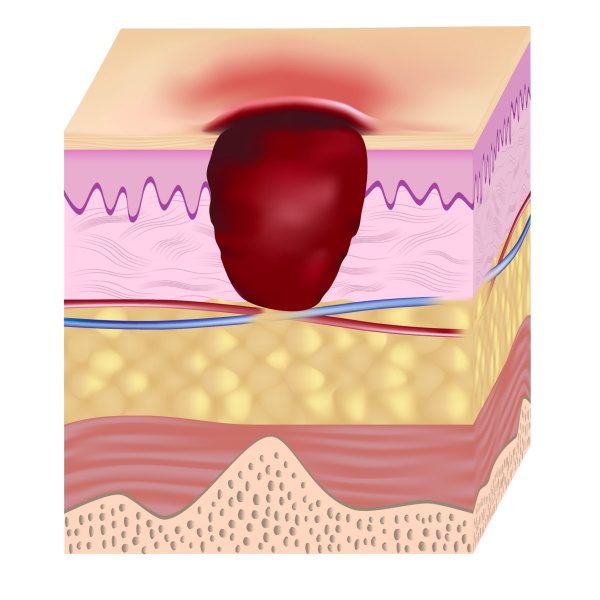
Treatment of stage 3 pressure sores
How to treat stage 3 pressure ulcers
Manage biofilm
Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution(10) is indicated for cleansing irrigation and moistening of acute and chronic wounds.
- Prevents infection(11)
- Helps to prevent biofilm formation
- Reduces healing time(12)
It moistens wound dressings and dissolves encrusted bandages or wound dressings during dressing changes.
Prontosan® Gel X(10) proper wound cleansing is essential. The use of Prontosan® Wound Gel X provides long-lasting cleansing and decontamination of the wound bed between dressing changes.
Prontosan® Debridement Pad(10) has been designed to support the wound bed preparation when used in conjunction with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
Treat local infection
Askina® Calgitrol® is a range of dressings with an ionic silver alginate matrix providing a broad spectrum antimicrobial effectiveness on infected wounds and preventing contamination from external bacteria.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Paste(13) is a dressing with an ionic silver alginate matrix in a paste form.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Thin(13) is a conformable ionic silver alginate matrix used as a wound bed interface.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Ag(13) integrates an ionic silver alginate matrix on an absorbent polyurethane foam dressing.
Manage wound odour
Askina® Carbosorb(13) is a conformable, sterile wound dressing combining two layers: an absorbent layer and an activated charcoal layer for the absorption of bacterial malodour.
Manage wound exudate
Askina® DresSil Sacrum(13), Askina DresSil(13), Askina® DresSil Border(13) help to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a perfored silicone wound contact layer, a highly absorbent polyurethane foam and a vapor permeable waterproof outer film. Indicated for pressure ulcers (PU), diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), venous leg ulcers (VLU) and 1st/2nd degree burns.
Askina® Foam(13) and Askina® Heel(9) help to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a polyurethane foam wound contact surface with high absorption capacity and a vapour permeable, water and bacteria resistant polyurethane film outer layer. Indicated for pressure ulcers (PU), diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), venous leg ulcers (VLU) and 1st/2nd degree burns.
Treatment of stage 4 pressure ulcers
How to treat stage 4 pressure ulcers
Manage biofilm
Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution(10) is indicated for cleansing irrigation and moistening of acute and chronic wounds.
- Prevents infection(11)
- Helps to prevent biofilm formation
- Reduces healing time(12)
It moistens wound dressings and dissolves encrusted bandages or wound dressings during dressing changes.
Prontosan® Gel X(10) proper wound cleansing is essential. The use of Prontosan® Wound Gel X provides long-lasting cleansing and decontamination of the wound bed between dressing changes.
Prontosan® Debridement Pad(10) has been designed to support the wound bed preparation when used in conjunction with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
Treat local infection
Askina® Calgitrol® is a range of dressings with an ionic silver alginate matrix providing a broad spectrum antimicrobial effectiveness on infected wounds and preventing contamination from external bacteria.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Paste(13) is a dressing with an ionic silver alginate matrix in a paste form.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Thin(13) is a conformable ionic silver alginate matrix used as a wound bed interface.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Ag(13) integrates an ionic silver alginate matrix on an absorbent polyurethane foam dressing.
Manage wound odor
Askina® Carbosorb(13) is a conformable, sterile wound dressing combining two layers: an absorbent layer and an activated charcoal layer for the absorption of bacterial malodour.
Manage wound exudate
Askina® DresSil Sacrum(13), Askina DresSil(13), Askina® DresSil Border(13) help to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a perfored silicone wound contact layer, a highly absorbent polyurethane foam and a vapor permeable waterproof outer film. Indicated for pressure ulcers (PU), diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), venous leg ulcers (VLU) and 1st/2nd degree burns.
Askina® Foam(13) and Askina® Heel(9) help to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a polyurethane foam wound contact surface with high absorption capacity and a vapour permeable, water and bacteria resistant polyurethane film outer layer. Indicated for pressure ulcers (PU), diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), venous leg ulcers (VLU) and 1st/2nd degree burns.
Wound care blog
Wound Care Blog
-
The Use of Prontosan Solution and Prontosan Debridement Pad in Kyperkeratosis on the Foot
Read MoreBeth Williams, High Risk Podiatrist, Manchester Local Care Organisation, shares her experience of using Prontosan Debridement Pad. This is adapted from an article originally presented at Wounds UK 7th – 9th November 2022
-
Clinical experience of the Prontosan® Debridement Pad
Read MoreIn 2021 an article reviewed 111 responses which were collected from 56 clinicians over a broad range of specialties including leg ulcer clinic staff, podiatrists and practice nurses asking their opinion on a microfibre debridement pad and how it performed in clinical practice
-
Wound Bed Preparation - A Practical Perspective
Read MoreKatie Bennett shares her experiences of using the Prontosan® wound bed preparation system for lower limb wound care.
References:
1) Gefen, A. How much time does it take to get a pressure ulcer? Integrated evidence from human, animal, and in vitro studies. HYPERLINK "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18927481"Ostomy Wound Manage. 2008 Oct;54(10):26-8, 30-5.
2) Range varies among settings and classification method.
- Bereded DT, Salih MH, Abebe AE. Prevalence and risk factors of pressure ulcer in hospitalized adult patients; a single center study from Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2018;11(1):847. Published 2018 Nov 29. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC626787
- Vanderwee K, Clark M, Dealey C, Gunningberg L, Defloor T. Pressure ulcer prevalence in Europe: a pilot study. J Eval Clin Pract. 2007;13(2):227-35. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17378869)
- Barrois B, Labalette C, Rousseau P, et al. A national prevalence study of pressure ulcers in French hospital inpatients. J Wound Care. 2008;17(9):373-6, 378-9. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18833894)
- Shahin ES, Dassen T, Halfens RJ. Pressure ulcer prevalence and incidence in intensive care patients: a literature review. Nurs Crit Care. 2008;13(2):71-9 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18289185)
- Vangilder C, Lachenbruch C, Algrim-boyle C, Meyer S. The International Pressure Ulcer Prevalence™ Survey: 2006-2015: A 10-Year Pressure Injury Prevalence and Demographic Trend Analysis by Care Setting. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2017;44(1):20-28.(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27977509)
3) Tinelli G, Sica S, Guarnera G, Pitocco D, Tshomba Y. Wound Care during COVID-19 Pandemic [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jun 24]. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020;S0890-5096(20)30545-8. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2020.06.044; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7311334
4) Haesler E (Ed.) EPUAP/NPIAP/PPPIA, (2019), Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: Quick Reference Guide. European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel and Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance
5) López-Pérez R, Gutiérrez Ibáñez B, Incidence of pressure ulcers (bed sores) in patients on treatment with hyperoxygenated fatty acids. (Asturias, Spain). Unpublished.
6) Instructions for use Linovera®
7) Jimenez Torres J. (2010), Acidos Grasos Hiperoxigenados (AGHO) en el tratamiento y prevencion de las ulceras por presion, ulceras vasculares y pie diabetico. Panorama actual del medicamento 2010; 34(336):695-701
8) Declair V, (1997), The usefulness of topical application of essential fatty acids (EFA) to prevent pressure ulcers. Ostomy Wound Manage 43(5):48-52, 54.
9) Colin D, Chomard D, Bois C, Saumet JL, Desvaux B, Marie M, (1998), An evaluation of hyper-oxygenated fatty acid esters in pressure sore management. J Wound Care 7(2):71-2.
10) Cf. Instruction for use: Askina® Heel, Askina® DresSil Border Lite, Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution, Prontosan® Gel X, Prontosan® Debridement Pad
11) Moore M, (2016), 0.1% Polyhexanide-Betaine Solution as an Adjuvant in a Case-Series of Chronic Wounds. Surg Technology International.
12) Bellingeri A, Falciani F, Traspedini P, et al, (2016), Effect of a wound cleansing solution on wound bed preparation and inflammation in chronic wounds: a single-blind RCT. J Wound Care. 25(3):160-168. doi:10.12968/jowc.2016.25.3.160.
13) Cf. Instruction for use: Askina® Calgitrol® Paste, Askina® Calgitrol® Thin, Askina® Calgitrol® Ag, Askina® Carbosorb, Askina® DresSil Sacrum, Askina® DresSil Heel, Askina® DresSil, Askina® DresSil Border, Askina® Foam, Askina® Sorb Rope, Askina® Barrier Cream, Askina® Barrier Film Spray, Askina® Barrier Film Swabs.
14) Downie F, Sandoz H, Gilroy P, Royall D, Davies S, (2013). Are 95% of hospital-acquired pressure ulcers avoidable?. Wounds UK. 9. 16-22.3