Restarting Elective Orthopaedic Surgery whilst helping to Keep Patients Safe through Digital Innovation.
Utilising technology to address reduced face-to-face patient contact.
The COVID-19 global pandemic has seen the healthcare sector evolve an increasingly digital response to reduce the amount of face-to-face contact with patients. This will no doubt continue into the future, not only to increase efficiency and reduce costs, but to also empower patients to have more control over their own health and care.
B. Braun Strategic Partnerships’ aim is to support the healthcare sector in returning to a new normal through creating digitally innovative pathways. From workforce and bed shortage to infection rates, our partnership models focus on reducing system costs and improving both patient outcomes and hospital provider efficiency.
COVID-19 led to changing circumstances within the hospital environment, prioritising beds for those fighting the virus. Most elective surgeries were postponed or cancelled, leaving patients waiting anxiously for long-anticipated and life changing hip or knee surgery.
As the situation improves and elective surgery restarts, it is crucial to reduce risks to orthopaedic patients by updating the standard orthopaedic pathway, reducing time spent in hospital, and to allow patients to recover in the comfort of their own home.
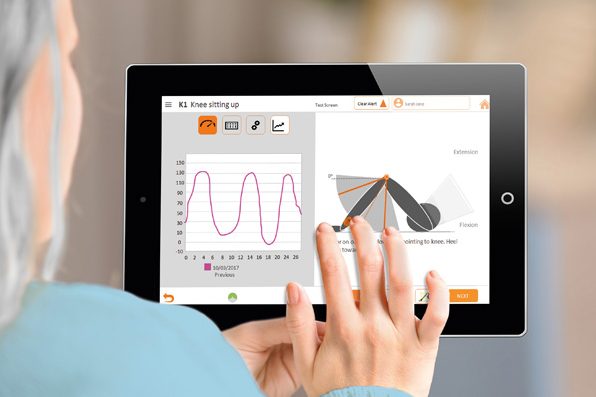
B. Braun’s Orthopaedic Pathway streamlines the care pathway through leveraging digital technology to give patients control of their own recovery and rehabilitation. A Range of Motion (ROM) sensor and downloadable app for the patient’s smartphone or tablet provides a digital platform for performing pre and post-operative physiotherapy exercises. Patients are able to visualise their ROM via an in-app avatar, track progress, log any pain during exercises and keep in contact with the hospital team via a two-way messaging function.
The communication channel with the hospital provides patients with support in their home environment, preventing the need for unnecessary hospital or at-home visits and allows for real time analysis of patients’ progress by the clinical team. Confidence in real time data on individual progress increases clinicians’ ability to discharge patients earlier from hospital. The majority of patients using the ROM sensor report that they feel secure as their physiotherapist could see their progress and find use of the ROM sensor beneficial.
Through the increased involvement in their own recovery, patients are empowered to carry out their flexion and extension exercises, accelerating their rehabilitation and reducing the need for outpatient and community physiotherapy appointments. Remotely analysing patients’ performance allows clinicians to tailor rehabilitation programmes to suit the individual; those who are achieving good range of motion can progress faster, and those who are having more problems can be prioritised to receive 1 on 1 care.
Within this time of crisis and beyond, digitisation is of growing importance within healthcare. From existing digital pathways such as The Orthopaedic Pathway, we can see that reducing pressure on existing systems, monetary savings and increasing patient satisfaction will be key outcomes of an increasingly digital healthcare system