Supracondylar Femur Osteotomy
OrthoPilot® aids correction of the leg axis during a supracondylar varus osteotomy of the femur (supracondylar femoral osteotomy, SFO). OrthoPilot® permits the precision performance of a medial closing-wedge SFO. This is possible through kinematic leg axis measurement with the aid of an infrared-assisted position transmitter.
The final axis ratios can be used to navigate to an exact degree and can be adjusted in real time. The most important criteria in the development of OrthoPilot® were its integration into the surgical procedure as well as the time for rollover of the procedure. Patient-friendly navigation is also of the utmost importance to us. From the very beginning, a method has been developed without burdensome or expensive CT or MRI images and with as little additional operation time as possible.
SFO Features
- CT-free
- Matched exactly to the procedure, ergonomic instruments
- Positioning of K-wires with navigation
- User-friendly navigation sequence that is easily integrated into the operation
- Intraoperative check and documentation of the axial ratio with OrthoPilot®
- Numerous international studies have confirmed significantly improved alignment
- Used routinely in more than 600 clinics
- More than 300 OrthoPilot® publications worldwide
Software Elements
Innovation
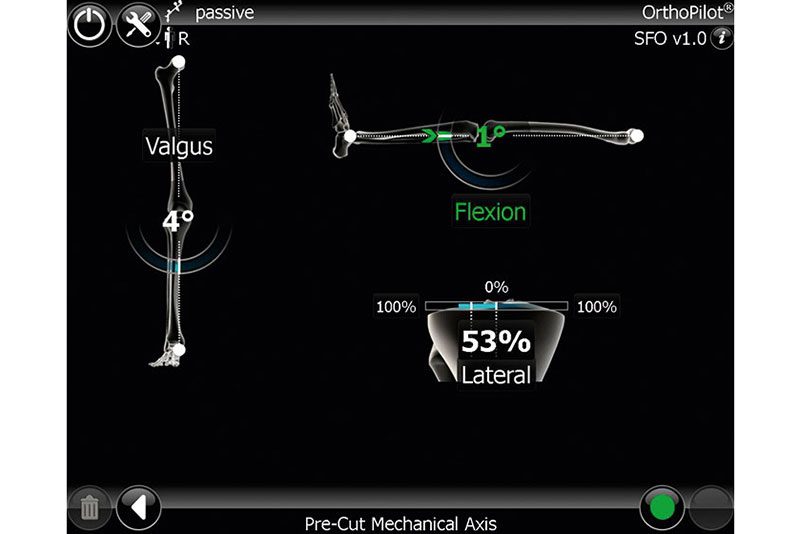
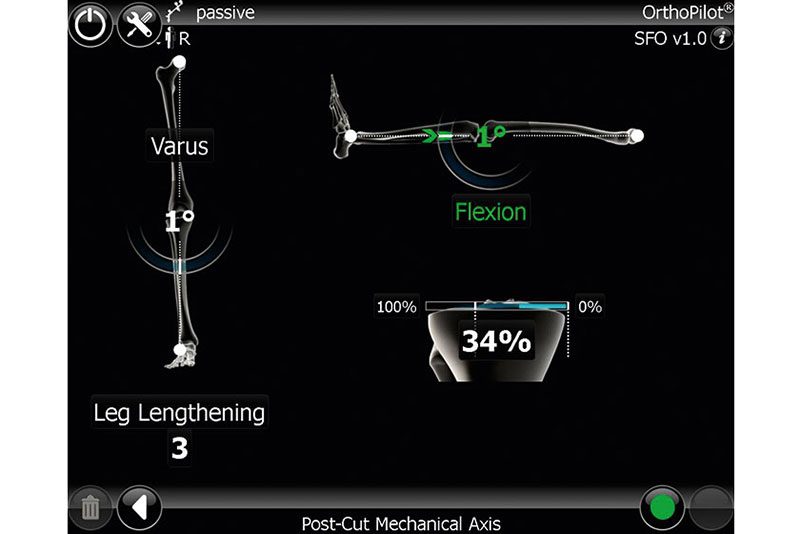
OrthoPilot® allows the precise execution of axis-correcting maneuvers in the closing-wedge SFO technique. This is established by continuous monitoring of the leg alignment by means of infrared position tracking. The final HKA angle can be navigated and adjusted by degree with high precision. The passive infrared sensor technology allows for wireless operation without artifacts in intraoperative radiography.
Perfection
The navigational fine-tuning of the leg alignment provides utmost reproducible accuaracy in SFO. The OrthoPilot® SFO procedure is independent from the osteosynthesis implant system being used. The intraoperative, dynamic goniometry of the current leg alignment is displayed, including the actual femorotibial angle for checking the present deformity and its correction. In frontal plane, stability of the collateral ligaments can be assessed through varus and valgus stress.