Management of diabetic foot complications
Risk of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes
A diabetic foot ulcer is a common complication of diabetes mellitus. 19 to 34 percent of people with diabetes will suffer from a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) at some point in their lives.(1) The risk of developing such an ulcer increases with time.
The top priority in treating the diabetic foot syndrome is to avoid a major amputation. Because currently, the majority of all foot and lower leg amputations are performed on patients with diabetes mellitus. It is estimated that up to a third of all patients with diabetes suffering from diabetic foot ulcers will undergo amputation.2)
Patients with diabetes are at risk of foot ulcerations due to both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy as well as macro- and microangiopathy.
Sensitivity tests to detect peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy (sensory and motor) is the most commoncause of foot ulceration. As many patients with sensory neuropathy suffer from altered or complete loss of sensation in their feet and legs, any cut or injury in this area can go completely unnoticed for days or weeks. Motor neuropathy may result in muscle weakness (muscle atrophy), which causes foot deformities and subsequently improper weight distribution. Tissue ischemia and necrosis may occur, causing ulcerations. Furthermore, autonomic neuropathy can lead to decreased sweating due to denervation of dermal structures. This in turn induces dry skin and creates fissures, which increase the risk of infection.
Different assessment methods are available to detect diabetic peripheral neuropathy:
- Doppler ultrasound(3)
- Tuning fork
- Monofilament(3)
Diabetic angiopathy
Another risk factor for the development of diabetic foot ulcers and infections is diabetic angiopathy. Larger arteries calcify (macroangiopathy) and the capillary basement membranes of smaller arteries thicken (microangiopathy), which can lead to impaired microcirculation.
Adaption of a holistic approach
Holistic approach(3)
Up to 85 percent of diabetic foot-related amputations can be prevented with a holistic approach(4) that includes:
- Optimal diabetes control
- Effective local wound care
- Infection control
- Pressure relieving strategies
- Restoration of pulsatile blood flow
There are many ways to classify diabetic foot lesions. Wagner’s classification is the most widely used grading system for diabetic foot lesions.
Management of diabetic foot ulcers
Depending on the extent of the tissue damage, diabetic foot ulcers are categorized into five grades.(6-10) Every grade requires a specific treatment.
Grade 0 diabetic foot
How to prevent diabetic foot ulcers
Correct or eliminate any underlying causes of DFU
- Prescribe an adequate diet
- Achieve optimal diabetic control including glycemic control, management of high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia
- Address physical traumas due to inadequate footwear
Grade 1 DFU
How to manage grade 1 diabetic foot ulcers
Protect from friction
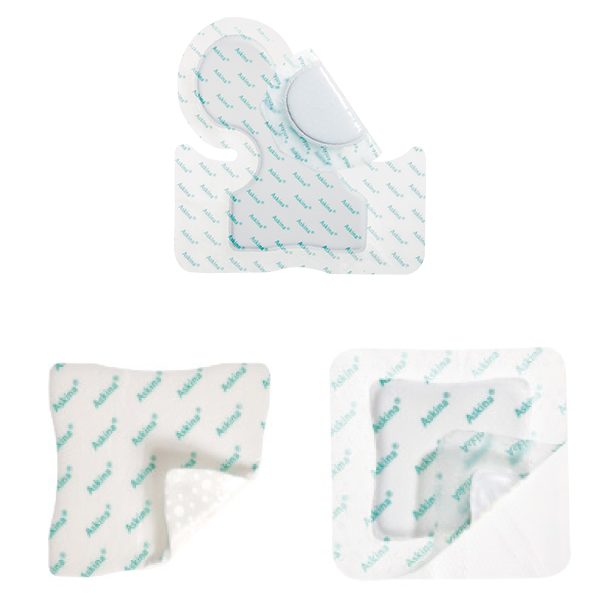
Askina® Heel(10) is a non adhesive hydrocellular heel dressing that protects the heel area from shear stresses and reduces pressure from external forces.
Manage biofilm
Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution(13) is indicated for cleansing irrigation and moistening of acute and chronic wounds.
- Prevents infection(14)
- Helps to prevent biofilm formation
- Reduces healing time(15)
It moistens wound dressings and dissolves encrusted bandages or wound dressings during dressing changes.
Prontosan® Gel X(10) proper wound cleansing is essential. The use of Prontosan® Wound Gel X provides long-lasting cleansing and decontamination of the wound bed between dressing changes.
Prontosan® Debridement Pad(10) has been designed to support the wound bed preparation when used in conjunction with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
Manage wound exudate
Askina® DresSil Heel(13) is a an absorbent, conformable silicone adhesive foam with an adehsive border. It protects the heel and malleolous and provides absorbancy for exuding wounds
Askina® DresSil®(13) is a self adherent foam dressing with soft silicone adhesive on one side and a vapor permeable waterproof film on the other.
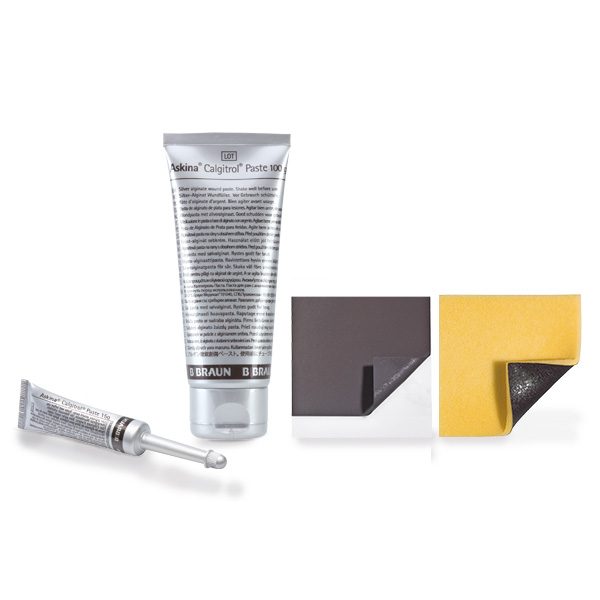
It may be combined with Askina® Calgitrol® Paste.
Manage local infection
- Askina® Calgitrol® Paste is a range of dressings with an ionic silver alginate matrix which in the presence of wound exudate helps maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions.
Grade 2 DFU
How to manage grade 2 diabetic foot ulcers
Manage biofilm
Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution(13) is indicated for cleansing irrigation and moistening of acute and chronic wounds.
- Prevents infection(14)
- Helps to prevent biofilm formation
- Reduces healing time(15)
It moistens wound dressings and dissolves encrusted bandages or wound dressings during dressing changes.
Prontosan® Gel X(10) proper wound cleansing is essential. The use of Prontosan® Wound Gel X provides long-lasting cleansing and decontamination of the wound bed between dressing changes.
Prontosan® Debridement Pad(10) has been designed to support the wound bed preparation when used in conjunction with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
Manage wound exudate
Askina® DresSil® (13) and Askina® DresSil® Border(13) help to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a perfored silicone wound contact layer, a highly absorbent polyurethane foam and a vapor permeable waterproof outer film.
Askina® DresSil Heel(13) is a an absorbent, conformable silicone adhesive foam with an adehsive border. It protects the heel and malleolous and provides absorbancy for exuding wounds
Manage local infection
Askina® Calgitrol® is a range of dressings with an ionic silver alginate matrix which in the presence of wound exudate helps maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Paste(13) is a dressing with an ionic silver alginate matrix in a paste form.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Thin(13) is a conformable ionic silver alginate matrix used as a wound bed interface.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Ag(13) integrates an ionic silver alginate matrix on an absorbent polyurethane foam dressing.
Manage wound odour
Askina® Carbosorb(13) is a conformable, sterile wound dressing combining two layers: an absorbent layer and an activated charcoal layer for the absorption of bacterial malodour.
Grade 3 DFU
How to manage grade 3 diabetic foot ulcers
Manage biofilm
Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution(13) is indicated for cleansing irrigation and moistening of acute and chronic wounds.
- Prevents infection(14)
- Helps to prevent biofilm formation
- Reduces healing time(15)
It moistens wound dressings and dissolves encrusted bandages or wound dressings during dressing changes.
Prontosan® Gel X(10) proper wound cleansing is essential. The use of Prontosan® Wound Gel X provides long-lasting cleansing and decontamination of the wound bed between dressing changes.
Prontosan® Debridement Pad(10) has been designed to support the wound bed preparation when used in conjunction with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
Manage wound exudate
Askina® Foam(13) helps to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a polyurethane foam wound contact surface with high absorption capacity and a vapor permeable, water and bacteria resistant polyurethane film outer layer.
Askina® DresSil Heel(13) is a an absorbent, conformable silicone adhesive foam with an adehsive border. It protects the heel and malleolous and provides absorbancy for exuding wounds
Manage local infection
Askina® Calgitrol® is a range of dressings with an ionic silver alginate matrix providing a broad spectrum antimicrobial effectiveness on infected wounds and preventing contamination from external bacteria.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Paste(13) is a dressing with an ionic silver alginate matrix in a paste form.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Thin(13) is a conformable ionic silver alginate matrix used as a wound bed interface.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Ag(13) integrates an ionic silver alginate matrix on an absorbent polyurethane foam dressing.
Manage wound odour
Askina® Carbosorb(13) is a conformable, sterile wound dressing combining two layers: an absorbent layer and an activated charcoal layer for the absorption of bacterial malodour.
Grade 4 DFU
How to manage grade 4 diabetic foot ulcers
Manage biofilm
Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution(13) is indicated for cleansing irrigation and moistening of acute and chronic wounds.
- Prevents infection(14)
- Helps to prevent biofilm formation
- Reduces healing time(15)
It moistens wound dressings and dissolves encrusted bandages or wound dressings during dressing changes.
Prontosan® Gel X(10) proper wound cleansing is essential. The use of Prontosan® Wound Gel X provides long-lasting cleansing and decontamination of the wound bed between dressing changes.
Prontosan® Debridement Pad(10) has been designed to support the wound bed preparation when used in conjunction with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
Manage wound exudate
Askina® Foam(13) helps to maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions with a polyurethane foam wound contact surface with high absorption capacity and a vapor permeable, water and bacteria resistant polyurethane film outer layer.
Askina® DresSil®(13) is a self adherent foam dressing with soft silicone adhesive on one side and a vapor permeable waterproof film on the other.
Askina® DresSil Heel(13) is a an absorbent, conformable silicone adhesive foam with an adehsive border. It protects the heel and malleolous and provides absorbancy for exuding wounds
Manage local infection
Askina® Calgitrol® is a range of dressings with an ionic silver alginate matrix providing a broad spectrum antimicrobial effectiveness on infected wounds and preventing contamination from external bacteria.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Paste(13) is a dressing with an ionic silver alginate matrix in a paste form.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Thin(13) is a conformable ionic silver alginate matrix used as a wound bed interface.
- Askina® Calgitrol® Ag(13) integrates an ionic silver alginate matrix on an absorbent polyurethane foam dressing.
Manage wound odour
Askina® Carbosorb(13) is a conformable, sterile wound dressing combining two layers: an absorbent layer and an activated charcoal layer for the absorption of bacterial malodour.
Grade 5 DFU
Wound care blog
Wound Care Blog
-
Prontosan® Debridement Pad | Before and After
Read MoreThe Prontosan® Debridement Pad is intended to support the soft mechanical debridement of chronic wounds in combination with Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution.
-
Award Winners! Integrating a Wound Cleansing Pathway into standard care.
Read MoreThe Doncaster Skin Integrity Team recently received a Bronze JWC award in the Infection and Biofilm category for their work on their local Wound Cleansing Pathway.
-
The role of Prontosan® in a pathway for biofilm based wound care
Read MoreAnita Kilroy-Findley, Clinical Lead Tissue Viability, Leicestershire Partnership NHS Trust, shares her experience of using the Prontosan in a pathway for biofilm based wound care.
References:
1) Everett E, Mathioudakis N. Update on management of diabetic foot ulcers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1411(1):153-165. doi:10.1111/nyas.13569. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5793889/
2) Kim SY, Kim TH, Choi JY, et al. Predictors for Amputation in Patients with Diabetic Foot Wound. Vasc Specialist Int. 2018;34(4):109-116. doi:10.5758/vsi.2018.34.4.109); https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6340693/
3) International Best Pratice Guidelines: Wound Management in Diabetic foot Ulcers. Wound International, 2013. https://www.woundsinternational.com/uploads/resources/33c16c714942cc022a74420bfdb5f3fd.pdf
4) Armstrong DG, Fisher TK, Lepow B, et al. Pathophysiology and Principles of Management of the Diabetic Foot. In: Fitridge R, Thompson M, editors. Mechanisms of Vascular Disease: A Reference Book for Vascular Specialists [Internet]. Adelaide (AU): University of Adelaide Press; 2011. 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534268/)
5) K Markakis, F. L. Bowling, A. J. M. Boulton. The diabetic foot in 2015: an overview. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016; 32(Suppl. 1): 169–178. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.2740
6) Pecoraro RE, Reiber GE, Burgess EM. Pathways to diabetic limb amputation. Basis for prevention. Diabetes Care 1990; 13(5):513-21
7) Wagner, FW. Foot Ankle, 2: 64-122, 1981
8) International Best Pratice Guidelines: Wound Management in Diabetic foot Ulcers. Wound International, 2013. https://www.woundsinternational.com/uploads/resources/33c16c714942cc022a74420bfdb5f3fd.pdf
9) Wounds UK. Best Pratice Statement : Ankle brachial pressure index (ABPI) in pratice. London : Wounds uk, 2019. Avalaibe to download from : www.wounds-uk.com
10) From Complex to Closure : Diabetic Foot Ulcer Assessment and Management Copyright © 2018 WoundSource & Kestrel Health Information, Inc. All rights reserved. www.woundsource.com/practice-accelerator
11) López-Pérez R, Gutiérrez Ibáñez B, Incidence of pressure ulcers (bed sores) in patients on treatment with hyperoxygenated fatty acids. (Asturias, Spain). Unpublished.
12) Instructions for use Linovera®
13) Cf. Instruction for use: Askina® Heel, Askina® Foam, Askina® Sorb, Askina® Sorb Rope, Askina® DresSil® Border, Askina® DresSil Border Lite, Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution, Prontosan® Gel X, Prontosan® Debridement Pad, Askina® Calgitrol® Paste, Askina® Calgitrol® AG, Askina® Calgitrol® THIN.
14) Moore M, (2016), 0.1% Polyhexanide-Betaine Solution as an Adjuvant in a Case-Series of Chronic Wounds. Surg Technology International.
15) Bellingeri A, Falciani F, Traspedini P, et al, (2016), Effect of a wound cleansing solution on wound bed preparation and inflammation in chronic wounds: a single-blind RCT. J Wound Care. 25(3):160-168. doi:10.12968/jowc.2016.25.3.160.